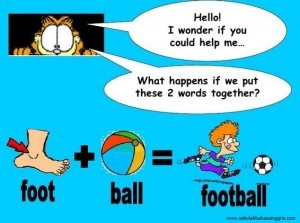
Question Word, Question Tag Dan Contoh Kalimatnya
www.sekolahbahasainggris.com– Pertanyaan yang jawabannya bukan berupa “yes atau no” dan digunakan untuk menanyakan bagian-bagian kalimat (S V O Adv)

| Menanyakan Subject (QW (+noun) + V+ O ?) | Menanyakan Object (QW (+noun) + aux + S ?) | |
| Subject/ Object | Who/what + V + (O) ?(+) Rika is sleeping.(+) They wash their cars.
(+) Cats have eaten my fish. |
Whom/what + Vaux + S + V?(+) Three people called you(+) They wash their cars.
(+) Cats have eaten my fish. |
| Kepemilikan | Whose + N + V + (O) ?(+) Their classrooms have been painted(+) Novita’s cat catches mice. | Whose + N + Vaux + S + V?(+) My teacher will visit my mother.(+) He borrwed Novita’s book. |
| Pilihan | Which/What + N + V + (O) ?(+) My beautiful sister is reading a famous novel.(+) Two book stores are being built near my house. | Which/What + N + Vaux + S + V?(+) My beautiful sister is reading a famous novel.(+) People built many departement stores. |
| Jumlah | How many + Nplural + V + (O) ?How much + UCN + V + (O)?(+) little water is in the bottle.
(+) Two book stores are being built near my house. |
How many + Vaux + S + V?How much + UCN + Vaux + S + V?(+) I met many people during the party.
(+) He drank much water. |
| Menanyakan Verb | Menanyakan Adverb (QW (+noun) + aux + S ?) | |
| What + aux + S + Do/ Doing/ Done ?(+) My beautiful sister is reading a famous novel.(+) I will go to her party
|
|
QUESTION TAG
- Pertanyaan singkat yang terletak di belakang, biasa menyertai kalimat affirmative (berita).
- Fungsi : sebagai penegas atau emphasizes dengan arti=…., kan?!
| No | SENTENCE | TAG | CONTOH |
| + | – | They have bought many clothes |
She has homework2.-+My sister doesn’t come
They have not been angry3.Negative words (seldom, never, hardly, rarely, little, few)+He seldom speaks English
She never found a reason4.Modal + / –/+Her brother can drive by himself
She will not be loved5.Indefinite pronoun thing
(anything, something, nothing, dst )ItEverything is not going to be Ok
Nothing is ipossible6.Indefinite pronoun person
(somebody, anybody, everybody, dst)theySomebody called her last night
Everybody is dancing7.Demonstrative singular (this, that)itThis is a big problem
That will be mine8.Demonstrative plural (those, these)theyThose are yours
These can be reasons9.TherethereThere are many ways
There is a man there10.Neutral : the doctor, student, baby,…heThe doctor did not operate the patient
Baby often cries in the night11.I am notam II am not a brave man
12.I amaren’t II am a new star
13.Let’s (let us)Shall weLet’s sing together
14.Imperative (perintah)Will youOpen the door
Let me know the story
Semoga Bermanfaat Para Pembaca SBI!!!